2025 W29 Global Market Recap
https://jasonhtmlshare.neocities.org/weekly%20updates/Global%20Equity%20Weekly%2020250721.html
Click to see a more reader friendly version of this content (点击查看视觉效果更好的版本)
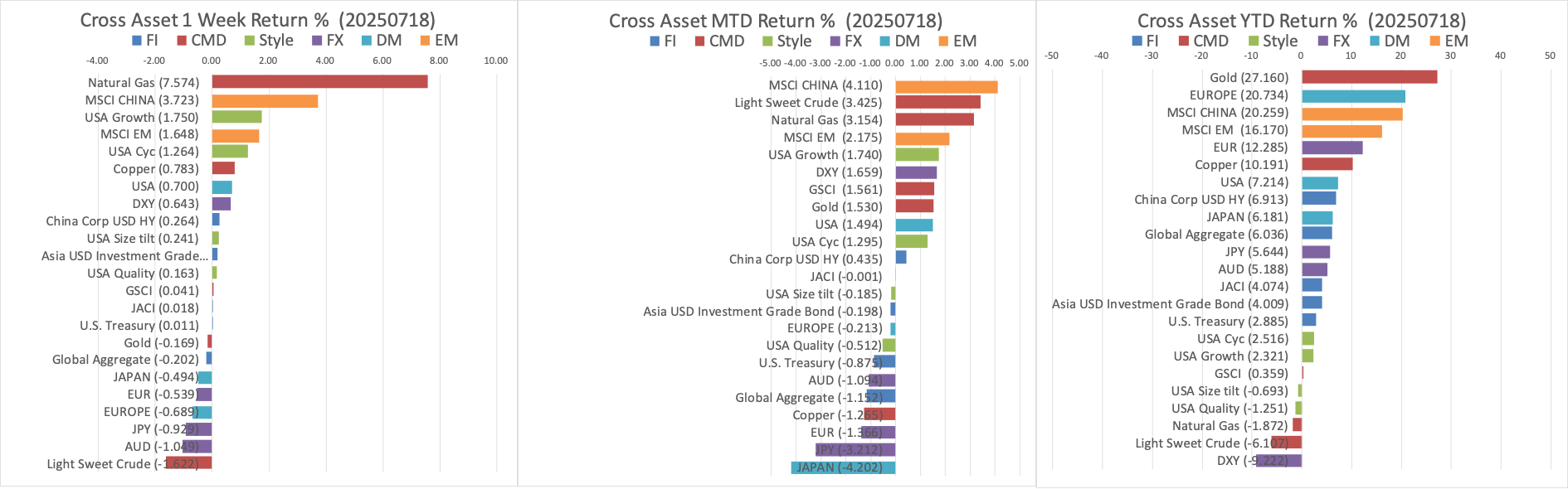
Cross Assets Performance
Markets Narratives
Markets overview
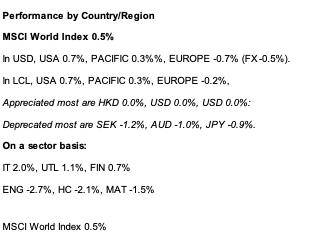
Overall Equity Market Performance
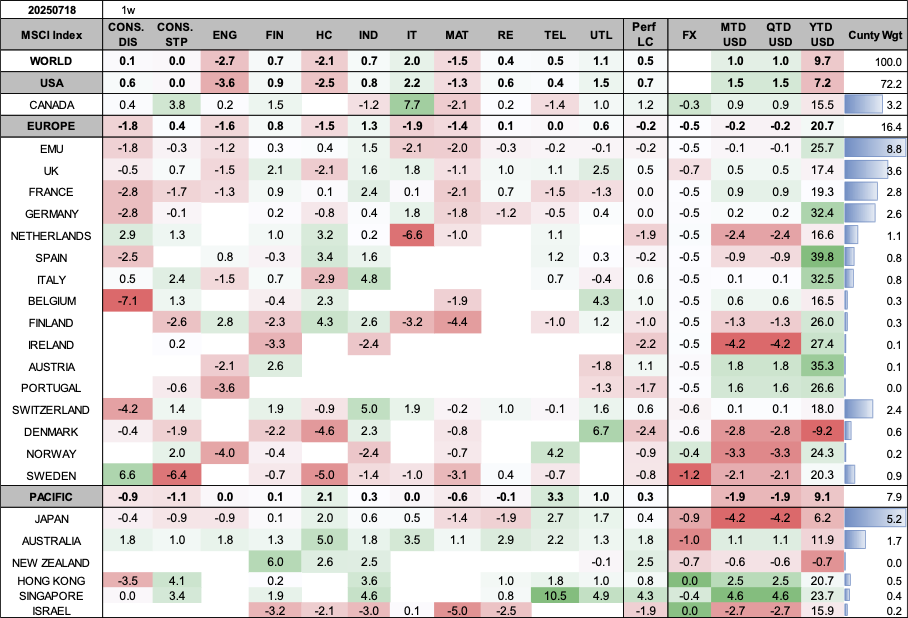
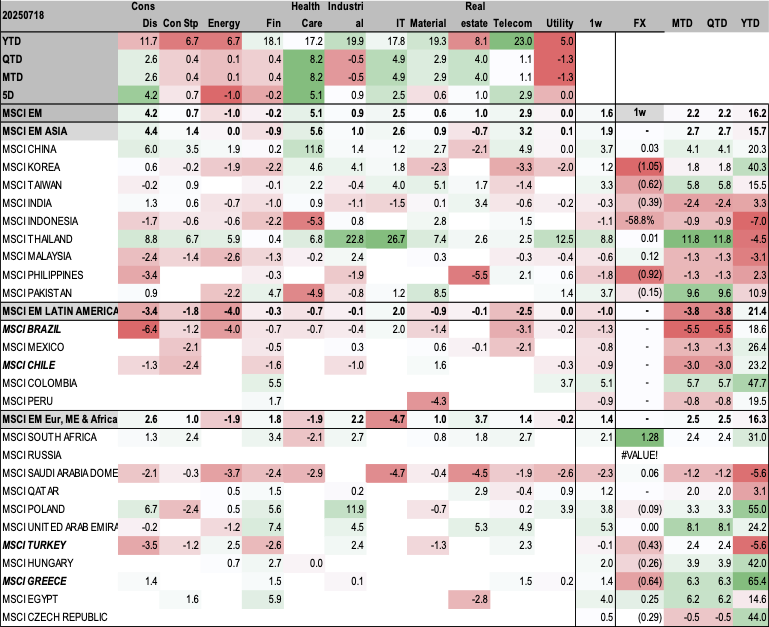
Market Review By Country
US Market Executive Summary
Consumer inflation heats up in U.S.
Solid corporate earnings bolster stocks
The S&P 500 Index and Nasdaq Composite Index reached new records during the week, supported by solid corporate earnings reports and generally favorable economic data. The small-cap Russell 2000 was also positive, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P Midcap 400 Index ended in negative territory.
Earnings season began in earnest on Tuesday with several big banks reporting earnings. JP Morgan Chase, the largest U.S. bank, and Citigroup both reported better-than-expected results for the second quarter. Then on Thursday, well-known consumer-facing names such as PepsiCo, United Airlines, and Netflix released reports that beat forecasts.
In other company-specific news, chipmaker NVIDIA announced that it had received permission from the Trump administration to sell its H2O artificial intelligence chips to China. NVIDIA, which hit the USD 4 trillion market capitalization level for the first time in early July, rallied on the announcement.
Inflation accelerates, while retail sales rebound
Stock investors also seemed to appreciate economic reports that pointed to consumer strength and inflation levels that, while not improving, didn’t seem too worrisome. Notably, the consumer price index (CPI) showed its biggest monthly increase in five months but generally matched consensus estimates.
CPI increased 0.3% month over month in June, up from 0.1% in May, with some economists pointing to higher tariffs as a driver of the price increases. On a year-over-year basis, prices rose 2.7%, up from May’s 2.4%. Core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy costs, increased 2.9% year over year, ticking up from 2.8% in May. Prices of household goods, recreational goods, and footwear have all accelerated since April. However, these increases were offset somewhat by lower car prices.
Investors were also focused on the Census Department’s retail sales report that showed sales up a better-than-expected 0.6% in June after falling 0.9% in May. Reports that President Donald Trump was planning to fire Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell put downward pressure on stocks on Wednesday, but the move was quickly reversed when Trump said he wasn’t going to remove Powell. Trump has been a fierce critic of the Fed chief as the central bank has paused further rate cuts so far this year.
Corporate bonds outperform Treasuries
Intermediate- and long-term U.S. Treasury yields finished the week little changed, while short-term yields marginally decreased amid speculation about Powell’s future at the Fed. (Bond prices and yields move in opposite directions.) The U.S. investment-grade corporate bond market outperformed Treasuries. Investment-grade corporate issuance was in line with expectations and was largely oversubscribed.
Europe Market Executive Summary
In local currency terms, the pan-European STOXX Europe 600 Index ended roughly flat as investors watched for signs of any progress in U.S. and European trade talks. Major stock indexes were mixed. Italy’s FTSE MIB gained 0.58%, while Germany’s DAX and France’s CAC 40 Index were little changed. The UK’s FTSE 100 Index rose 0.57%, helped partly by the depreciation of the UK pound against the U.S. dollar. A weaker pound lends support to the index because many of its companies are multinationals that generate meaningful overseas revenue.
UK inflation worse than expected; unemployment higher; wage growth slows
The annual rate of consumer price inflation in the UK unexpectedly rose to 3.6% in June from 3.4% in May, the fastest pace since January 2024. Higher prices for transport, especially motor fuels, drove the increase. Services inflation—a key metric for the Bank of England—stayed at 4.7%, indicating persistent underlying cost pressures. The consensus expectation had been for services inflation to ease.
The UK labor market appeared to cool further in the three months through May. The unemployment rate ticked higher to 4.7% from 4.6% in the three months through April, the highest level in four years. The number of payrolled employees declined by an estimated 41,000 in June, after a drop of 25,000 in May. Meanwhile, annual pay growth excluding bonuses was slightly higher than analysts had expected, coming in at 5.0%. This latest figure was down from an upwardly revised 5.3% the previous month.
Eurozone industry output expands; trade surplus widens more than expected
Industrial production in the euro area expanded by 1.7% sequentially in May, rebounding from the 2.2% decline recorded in April and beating market expectations for a rise of 0.9%. Increased output of energy, capital goods, and nondurable consumer goods drove the expansion. Year over year, output accelerated to 3.7% from 0.2% in the prior month.
Separately, the bloc’s trade surplus widened to EUR 16.2 billion in May from EUR 12.7 billion a year earlier, as exports rose 0.9% and imports fell 0.6%.
German investor sentiment highest in three years
The ZEW index of economic sentiment in July rose for a third consecutive month, coming in at 52.7—its highest level since February 2022. Analysts in a FactSet survey had expected a reading of 50.2. The economic research institute said almost two-thirds of experts polled called for the economy to improve, thanks to potential stimulus and expectations for a speedy resolution to the European Union’s trade dispute with the U.S..
Japan Market Executive Summary
Japan’s stock markets registered modest gains over the week, with the Nikkei 225 Index rising 0.63% and the broader TOPIX Index up 0.40%. Returns were capped by political uncertainty ahead of Japan’s Upper House election on July 20, where a possible outcome could be that Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba’s ruling Liberal Democratic Party-Komeito coalition fails to retain majority control.
Investors’ focus is likely to be on how pro-economy and reformative the new cabinet will be, as well as how dovish or hawkish a fiscal policy it adopts. The yield on the 10-year Japanese government bond rose to 1.53% from 1.49% at the end of the previous week on investor expectations that the election could result in a more fiscally dovish cabinet that seeks to increase government spending. The yen weakened to around the middle of the JPY 148 against the USD range, from a prior JPY 147.4.
Inflation cools
Inflationary pressures showed some signs of easing, as Japan’s core consumer price index (CPI) rose 3.3% year on year in June, less than consensus estimates for a 3.4% increase and down from 3.7% in May. The softening in core inflation was due mainly to falling contributions from energy, reflecting government subsidies.
On the trade front, with U.S. tariffs weighing on foreign demand, Japan’s exports fell 0.5% year on year in June, the second monthly drop and short of consensus estimates of a 0.5% increase. Exports to the U.S. declined sharply due to weaker shipments of autos, auto parts, and pharmaceuticals, and sales to China also fell. The U.S. has announced that it will implement a 25% reciprocal tariff on Japanese imports, effective August 1; however, bilateral trade talks between the two countries are ongoing, where a formal deal could be reached.
China Market Executive Summary
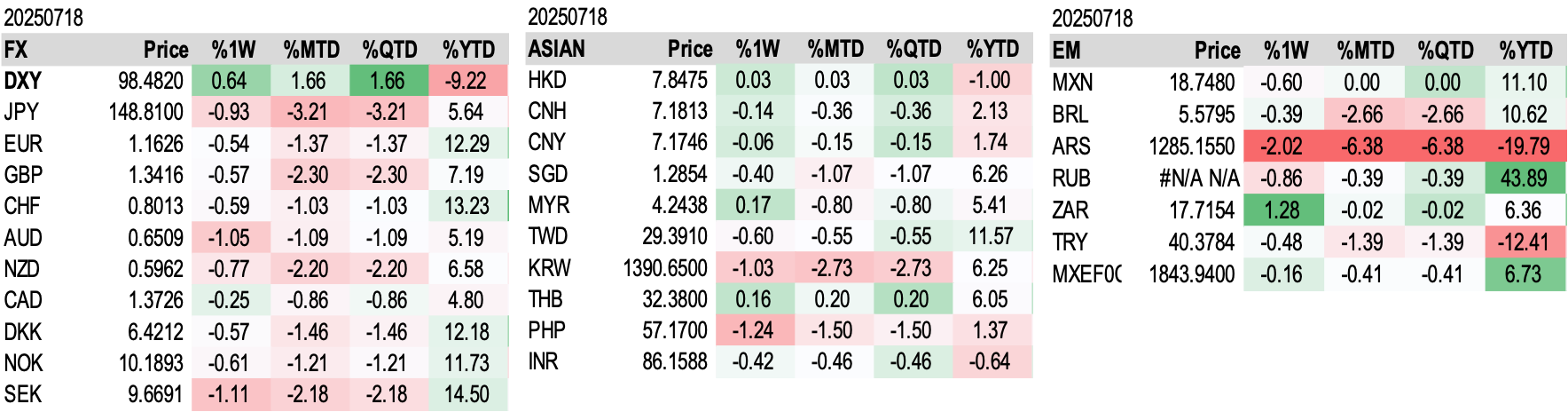
Foreign Exchange Performance
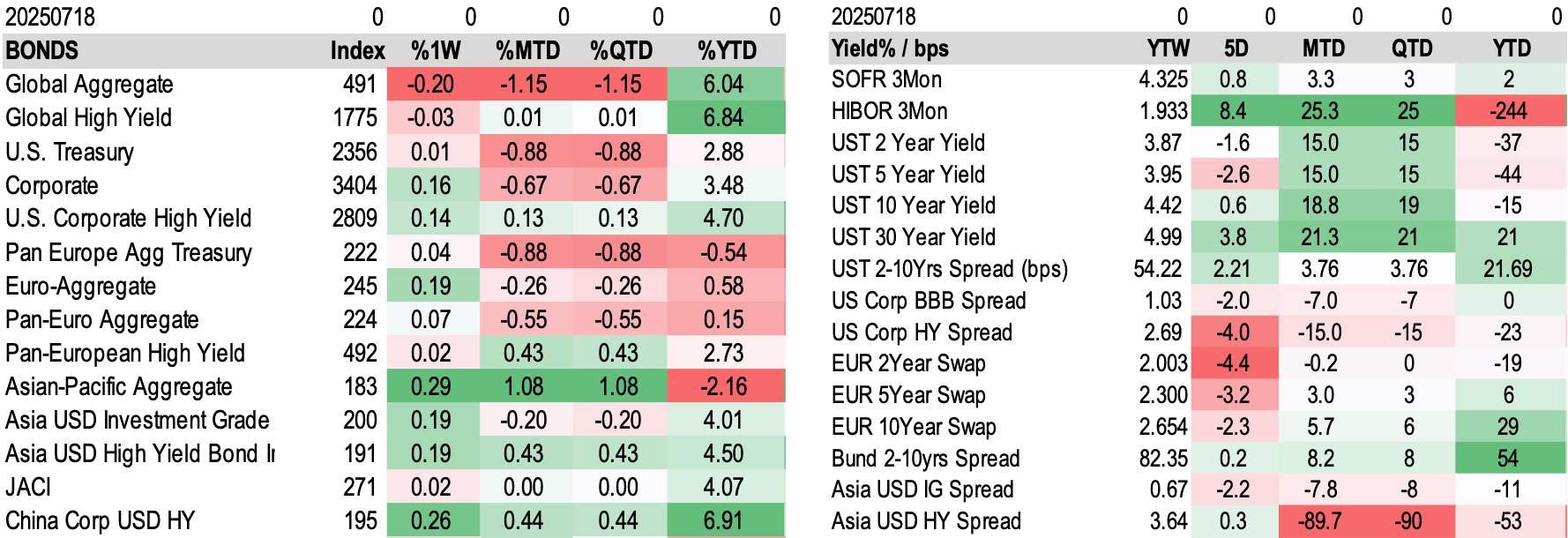
Fixed Income Performance
Earnings Revisions
(This image need to be displayed with 60% of its original scale (both height & width))
FactSet Updates: Earnings Consensus
FactSet Weekly Report
This Week's Focus: Are Magnificent 7 companies still the primary contributors to S&P 500 Q2 earnings growth?
- The answer is affirmative. Magnificent 7 companies remain a significant driver of S&P 500 earnings growth.
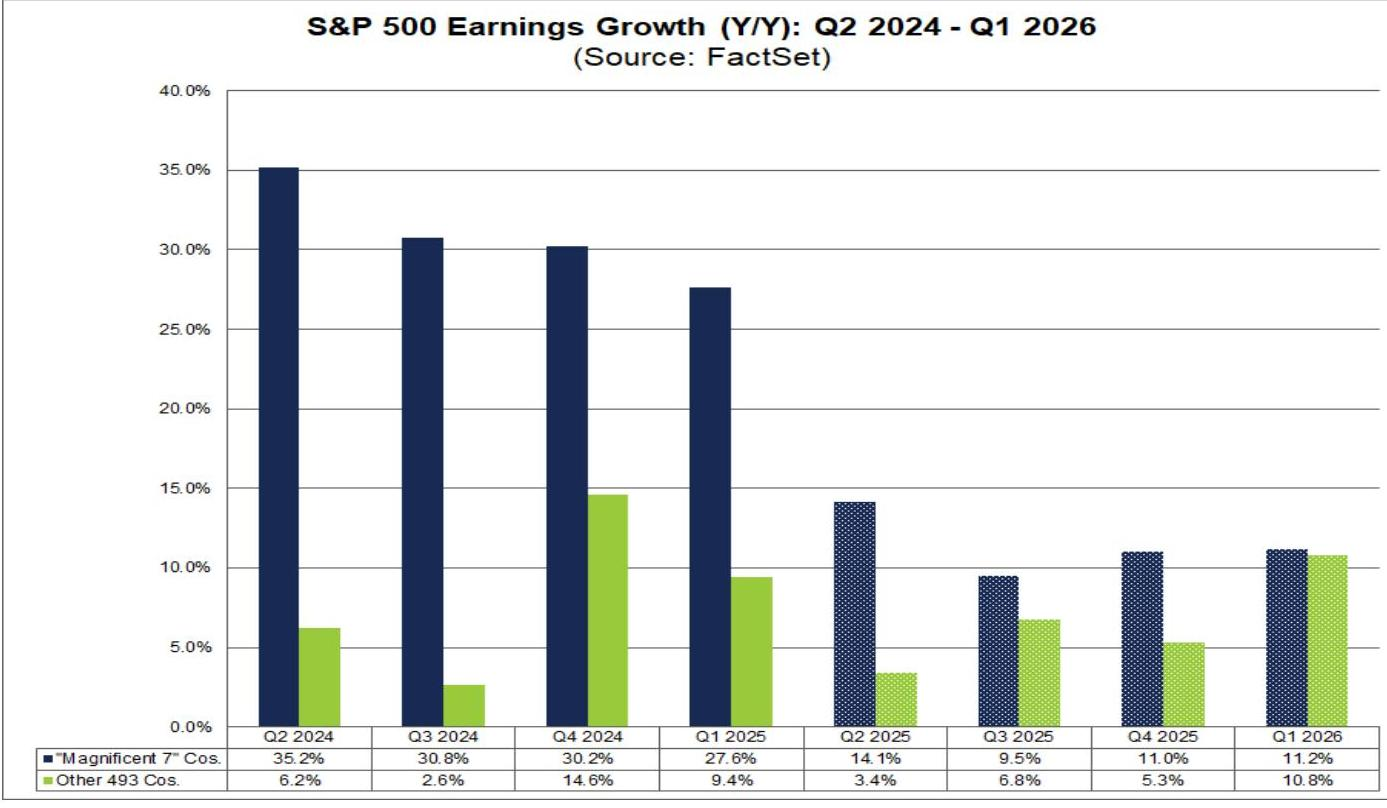
- The overall S&P 500 earnings growth rate for Q2 2025 is 5.6% year-over-year.
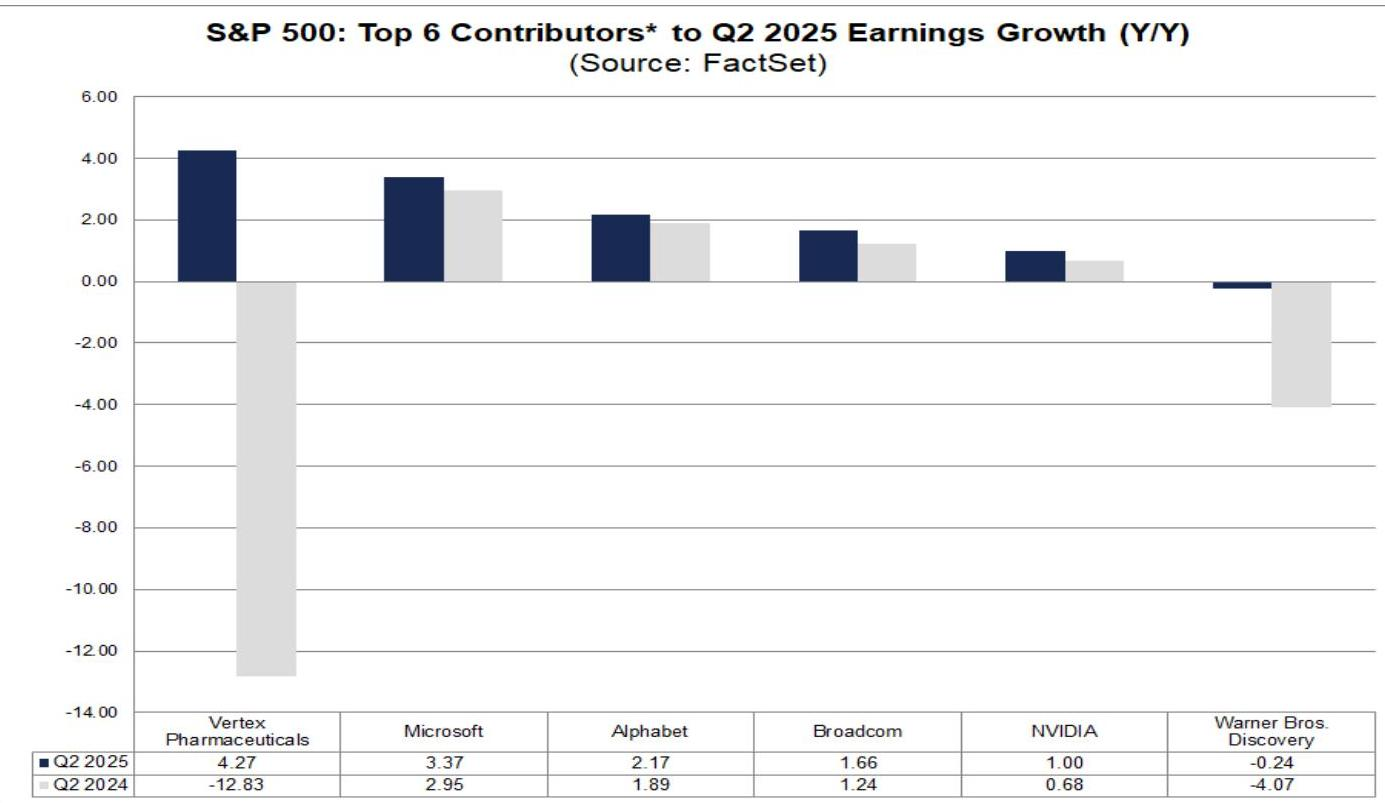
- The top six companies contributing most to the S&P 500's second-quarter earnings per share (EPS) year-over-year growth (listed in order of contribution) are: Warner Bros. Discovery, NVIDIA, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Microsoft, Broadcom, and Alphabet.
- Among these, NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Alphabet belong to the Magnificent 7 companies.
- Warner Bros. Discovery and Vertex Pharmaceuticals benefited from lower bases in the prior year period, primarily due to expenses and charges incurred then.
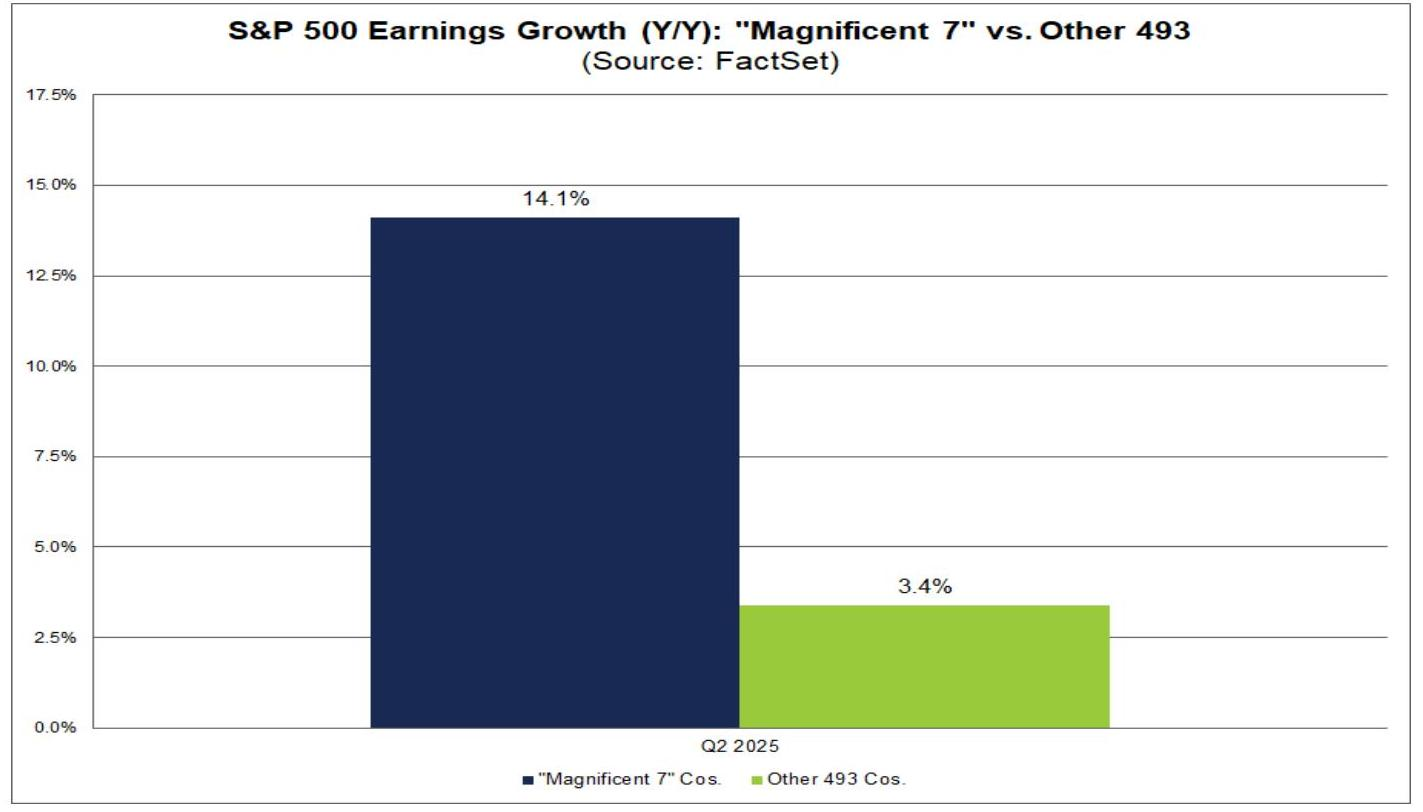
- Q2 2025 S&P 500 Earnings Year-over-Year Growth: Magnificent 7 vs. Other 493 Companies
- Q2 2025 Top Six S&P 500 Earnings Year-over-Year Growth Contributors (not listed by contribution order)
- Overall, the Magnificent 7 companies are expected to achieve 14.1% year-over-year growth in the second quarter.
- Excluding these seven companies, the blended earnings growth rate for the remaining S&P 500 companies (493 companies) is projected at 3.4%.
- Looking ahead, analysts anticipate a moderation in earnings growth for the Magnificent 7 companies over the next three quarters compared to Q2 2025.
- Conversely, analysts expect an acceleration in earnings growth for the remaining 493 companies over the next three quarters compared to Q2 2025.
- S&P 500 Annual Earnings Year-over-Year Growth: Q2 2024 to Q1 2026
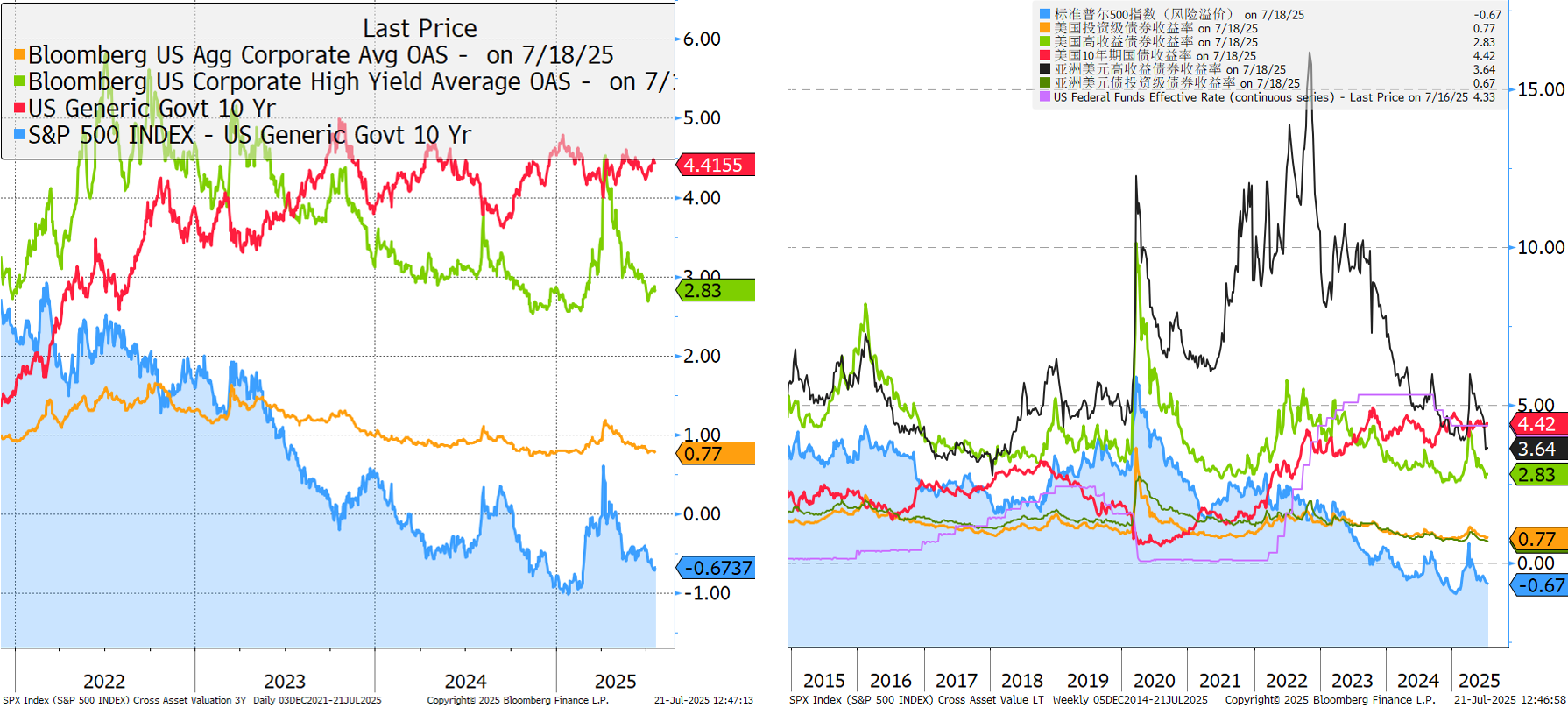
Cross assets valuation
Style relative valuation
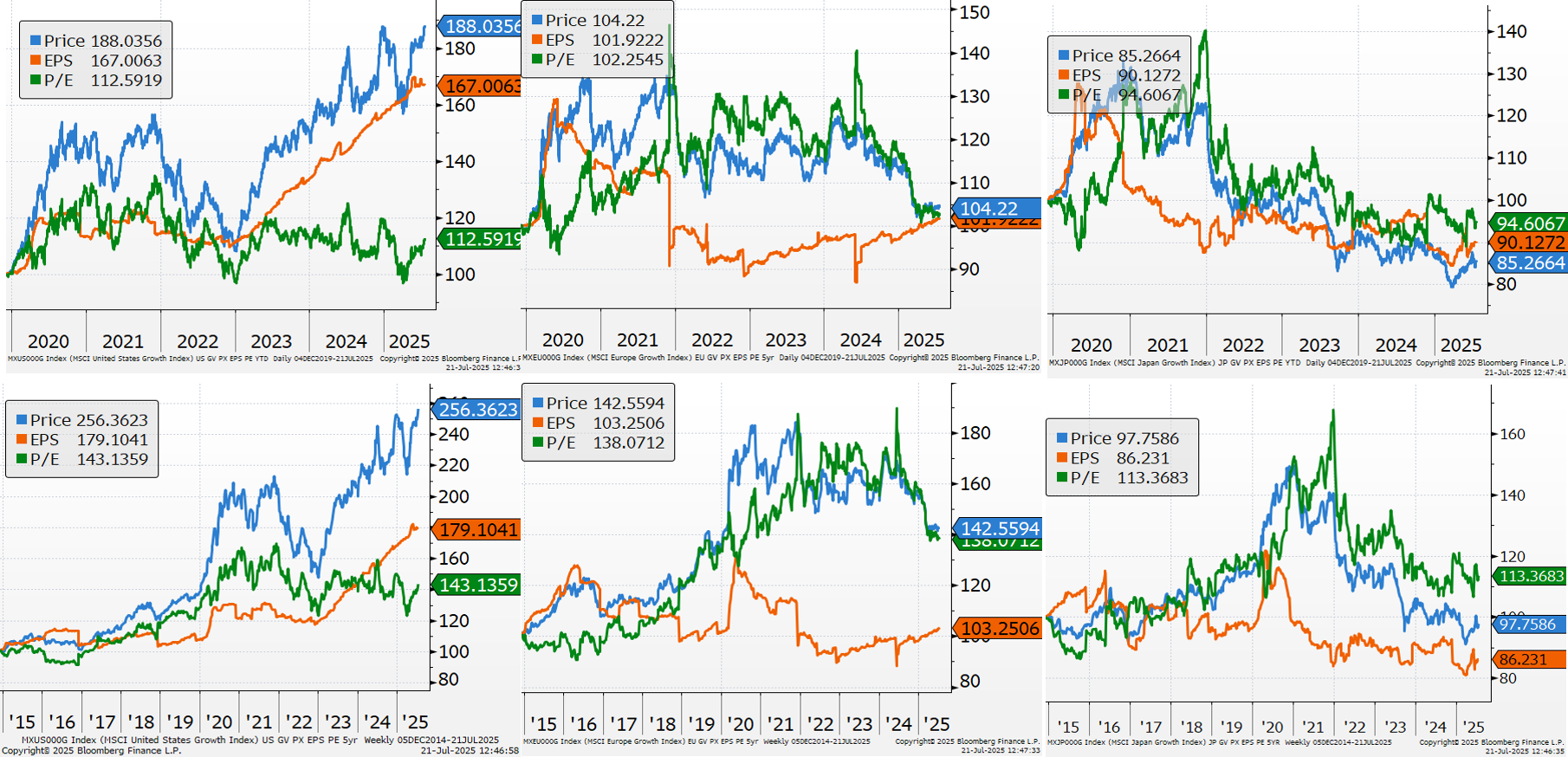
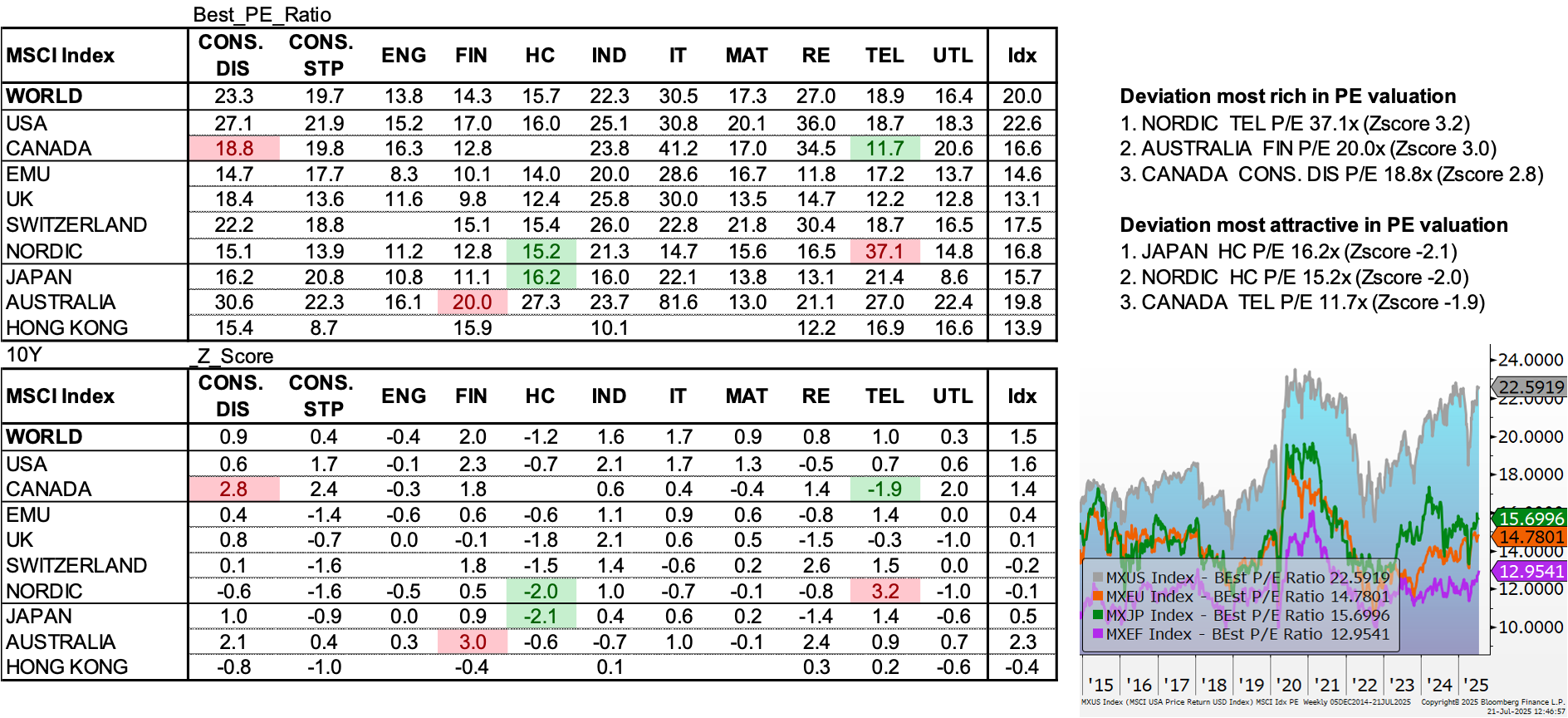
P/E ratios
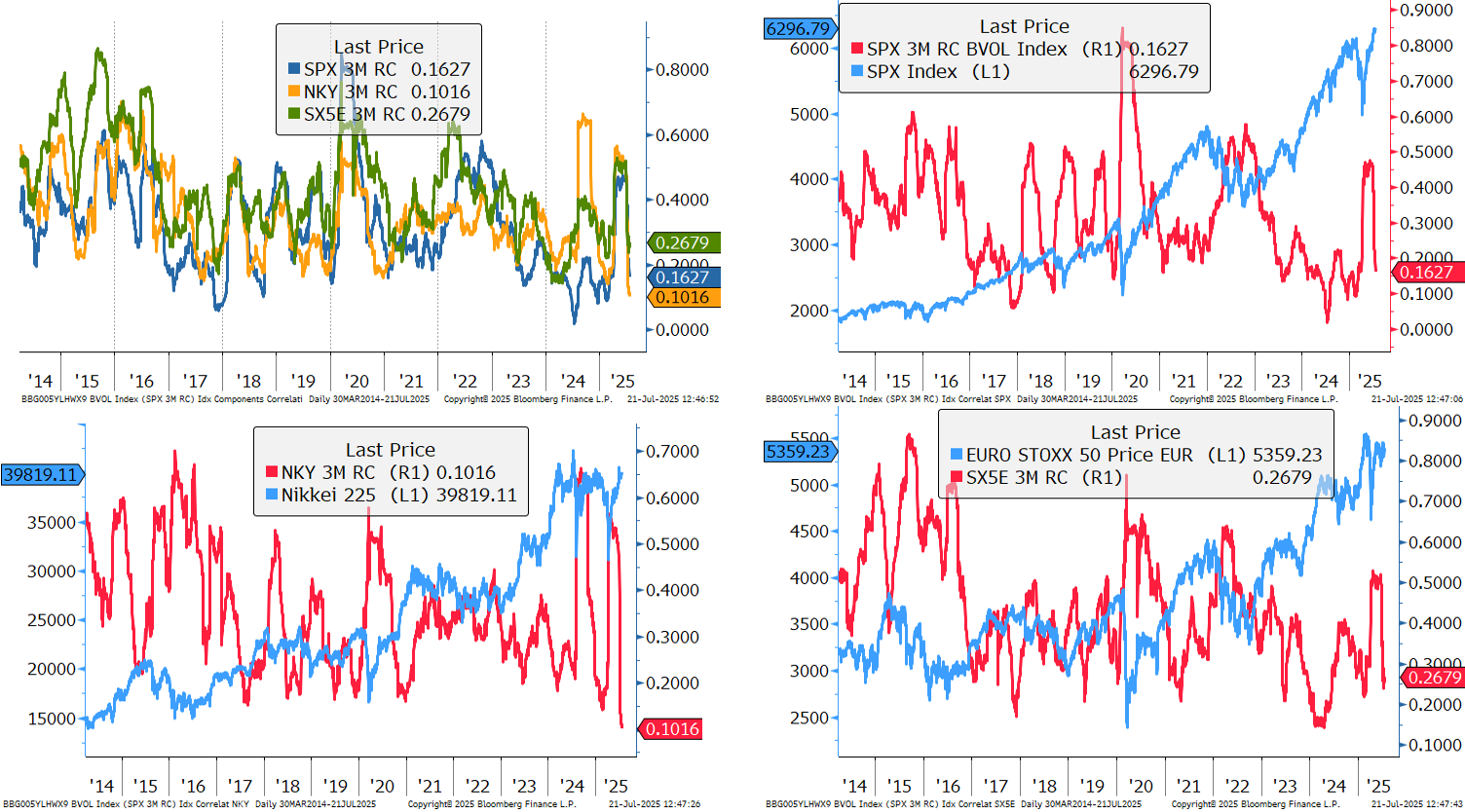
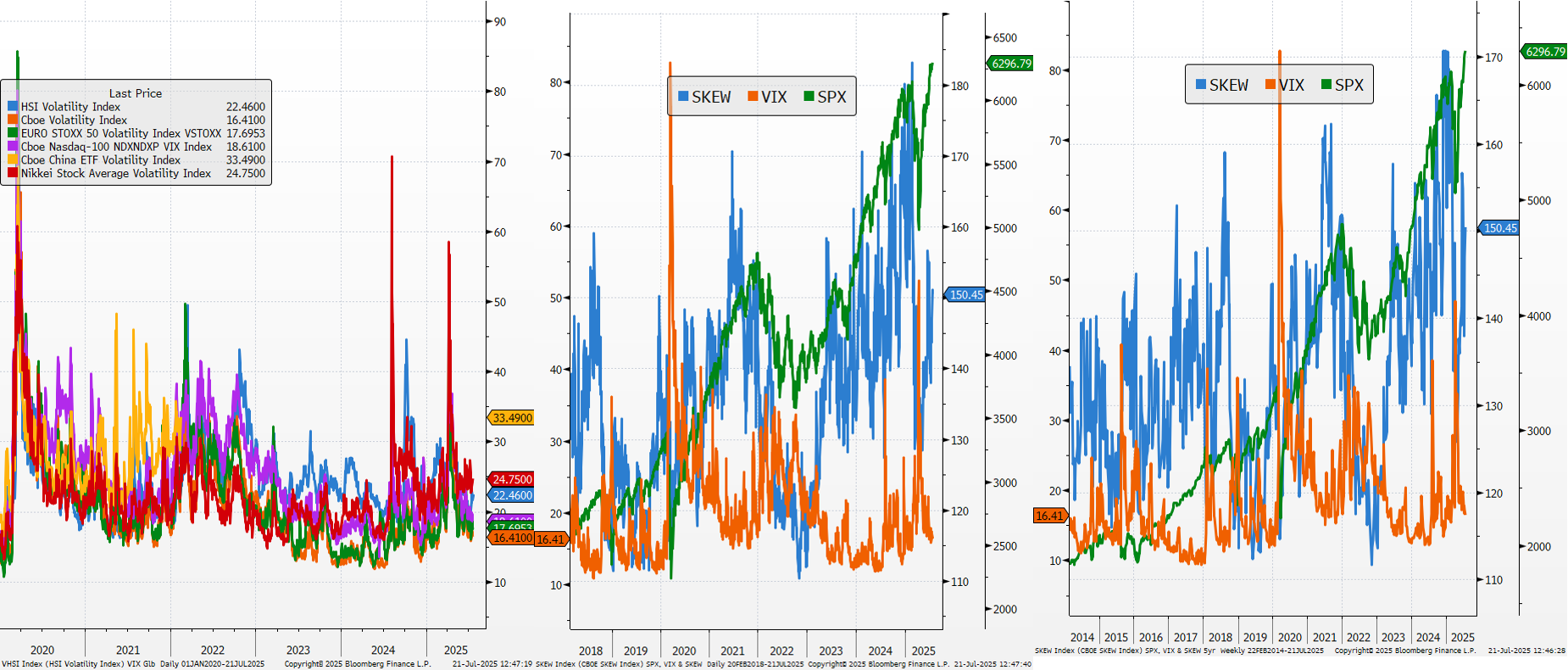
VIX and Skew
Intra Market Dynamics